The Parana delta is located in Argentina. The delta flows into the Rio de la Plata and has a length of 2570 km.
It is one of the biggest wetland systems in Argentina.
The delta is densely populated with many large cities, such as Buenos Aires, along or close to it.
The delta is also important because it is in a good strategic location for trade (Delta Alliance, n.d.).
The urban areas in the Parana Delta have been growing for some time now.
A great example is the Argentine capital Buenos Aires.
As can be seen, since 1985 Buenos Aires has expanded significantly due to its population growth.
The islands surrounding Buenos Aires are not yet considered part of Buenos Aires,
but the more space is needed for urban expansion,the more the availability of urban space is challenged,
and the more land in the delta is used for these expansions. This urban development brings about radical
changes in land use that challenge both the ecological and social sustainability of the delta region.
(Hedlund, 2015)
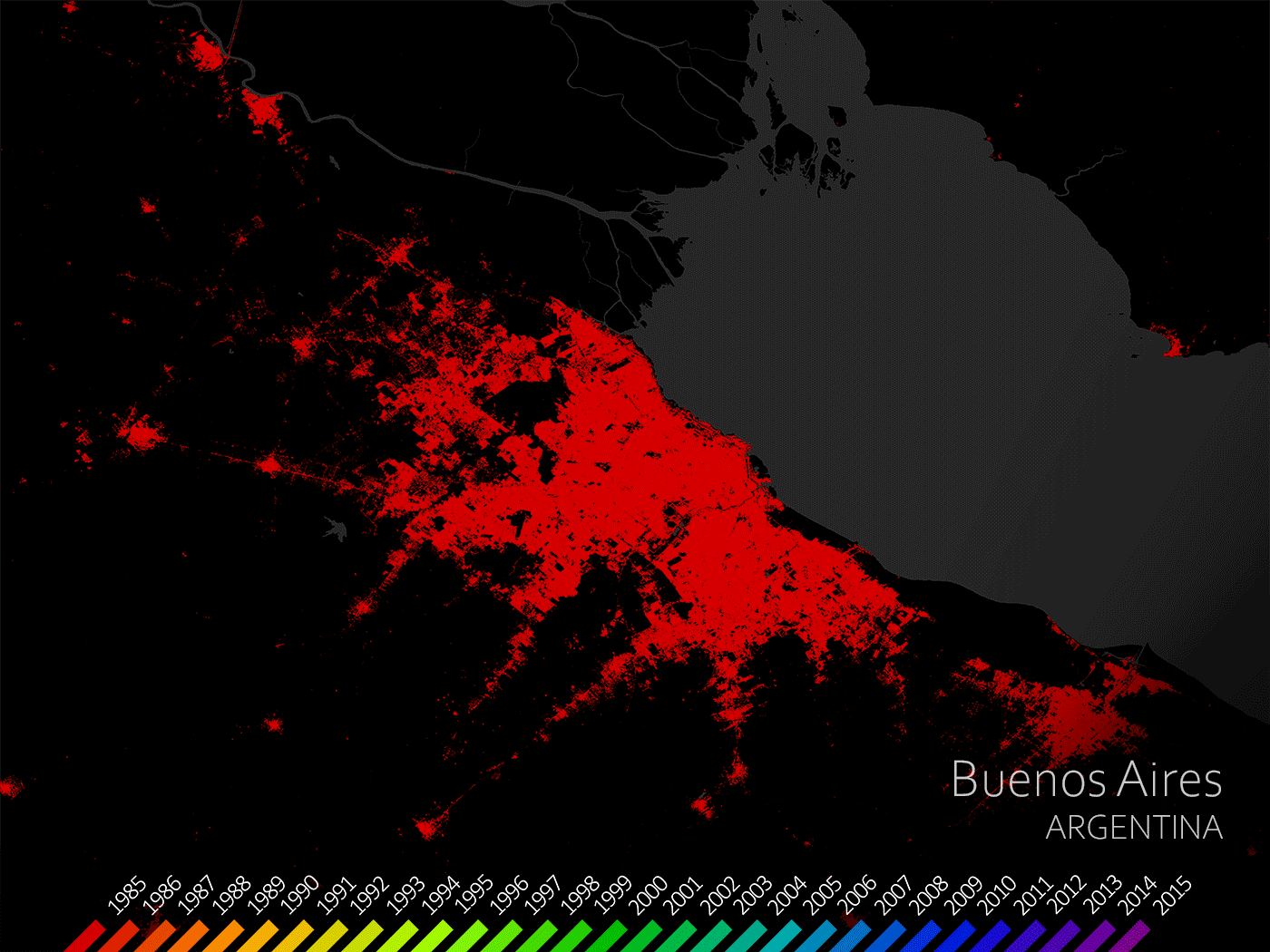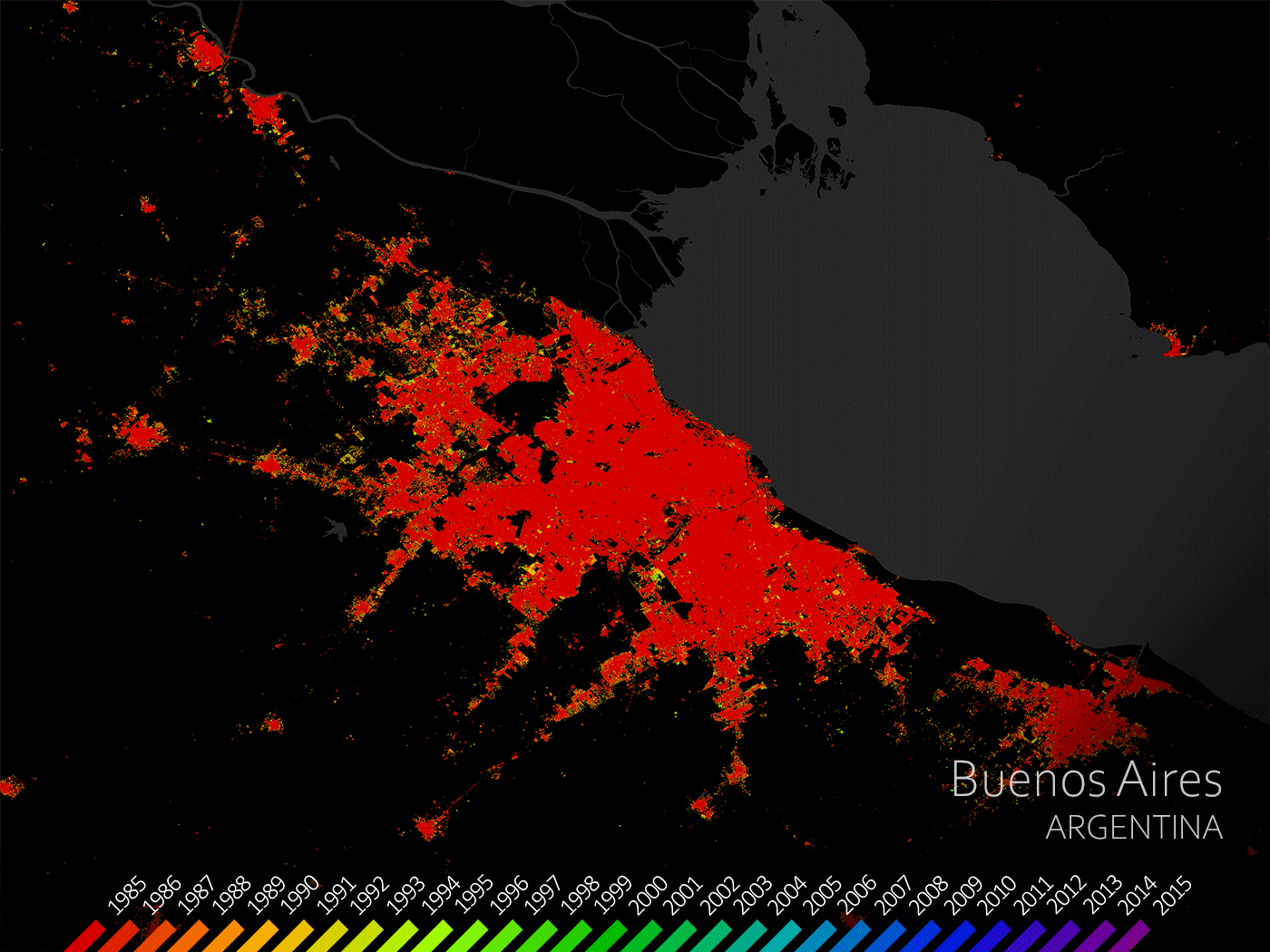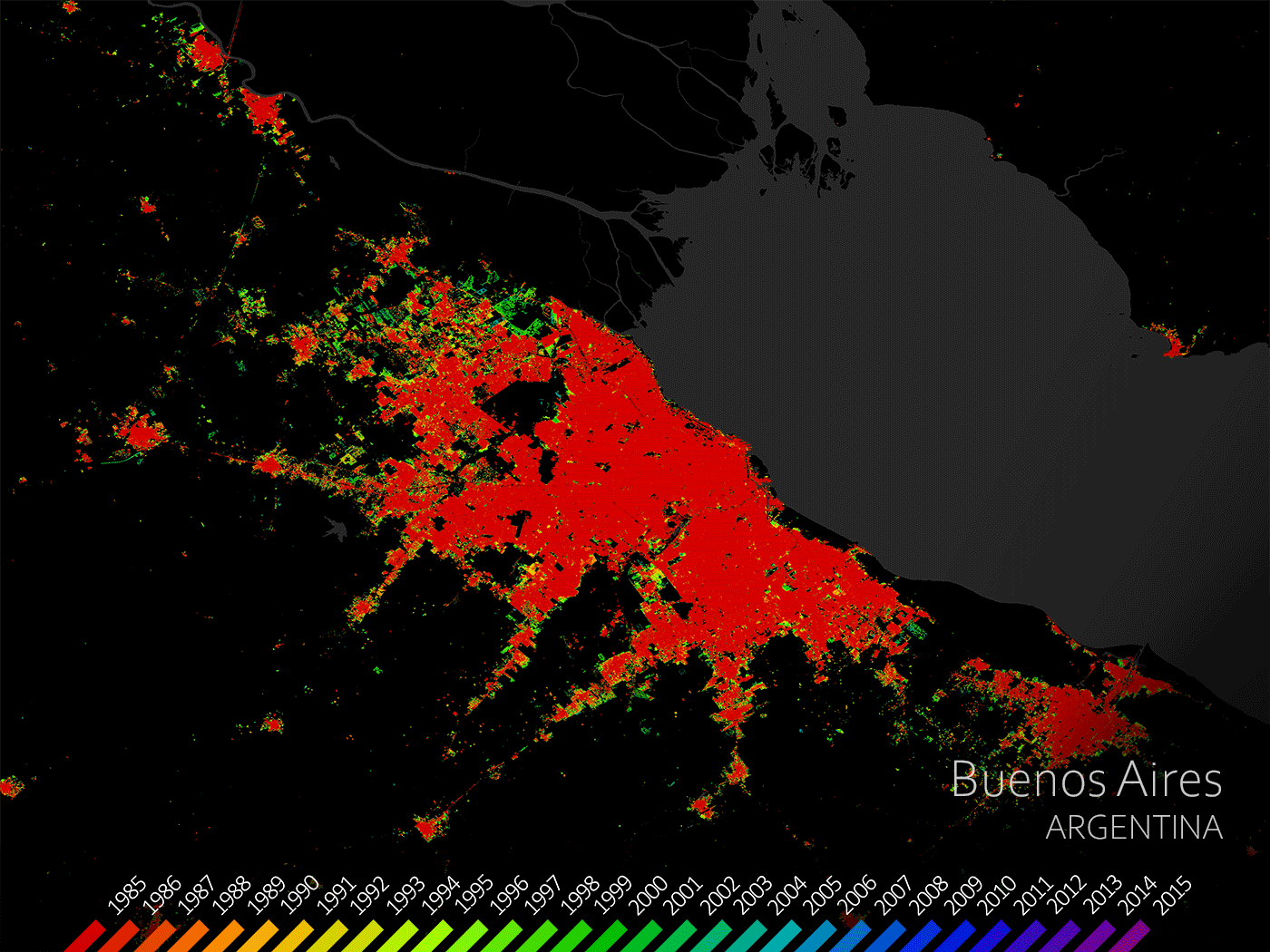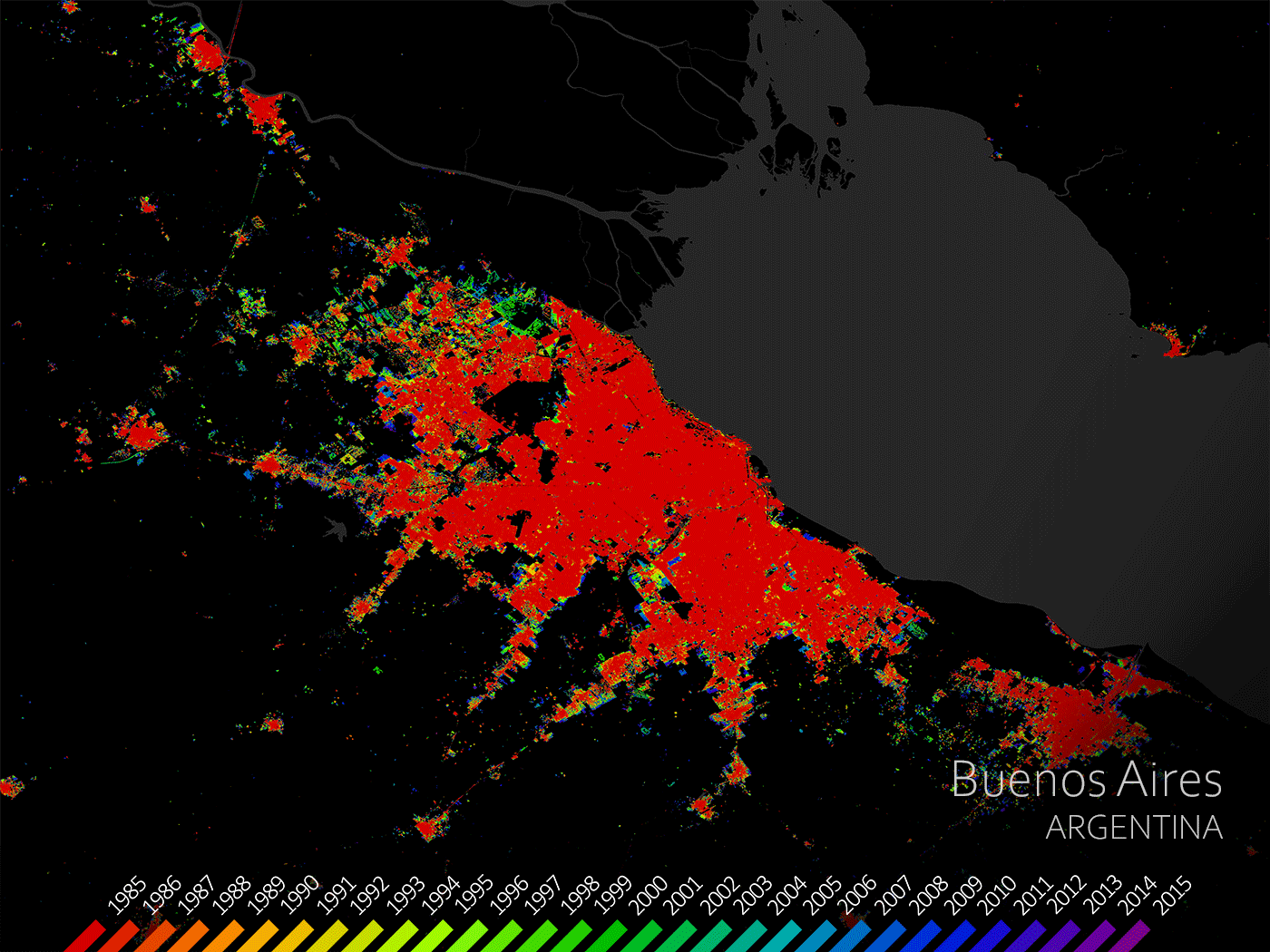
Buenos Aires, Argentina (The European Space Agency, 2021)
With urban populations growing faster than those in rural areas, urbanisation is the main driver of land loss in the deltas.
In 1985, only 3% of the country was urban, and in 2015 this doubled to 6%.
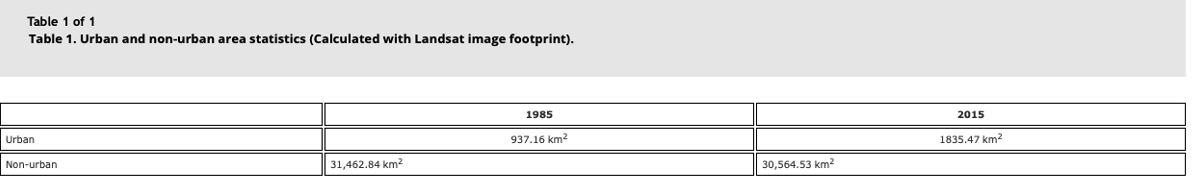
Urban and non-urban areas in km2 (Li, 2017).
In de periode van 1985 tot 2015 is er zo een 30,28% aan landbouwgrond in het gebied verloren gegaan door stedelijke uitbreidingen (Li, 2017).
When looking for solutions to the loss of agricultural land, one must
look in at other ways of urbanisation that ensure that the ecological
system is not or hardly affected.
A better, more environmentally friendly and more achievable way would
be to increase the concentration of the population instead of dividing
it up and developing new pieces of land (Li, 2017).
