Volta delta
Deltas
The Volta Delta is largely centered in Ghana. The river flows into the Atlantic Ocean near the coastal town of Ada Foah. The river originally consists of two rivers: the Black Volta and the White Volta. The river itself has a catchment area of six African countries but flows largely through Burkina Faso and Ghana.
Ghana
As a country, Ghana is one of the leading nations despite its small area and population. This is due to the fact that it was one of the first countries to gain independence from colonial rule. Ghana, of course, has much more to offer. It has beautiful and lush nature, a variety of biodiversity, and a picturesque coastline.
In addition, there are different types of soil present. This is due, among other things, to the savannahs that are found in Ghana. The climate is also an important factor. The climate is determined by two air masses: the continental air mass and the tropical air mass. This helps to ensure that the country generally has a tropical savannah climate. (Maier, s.d.)

Image 1: Savannah. Acquired from https://unsplash.com/photos/xuRE8JcuzKk
Impact of erosion
The coastline of Ghana and the Volta Delta consists of various elements, such as sand, clay & gravel. Together with the waves, they form the coastline. Erosion plays a major role in this and that is because of the waves that can play a dominant role. This ensures that it can be classified as wave-dominated in Galloway's 1975 delta classification diagram.
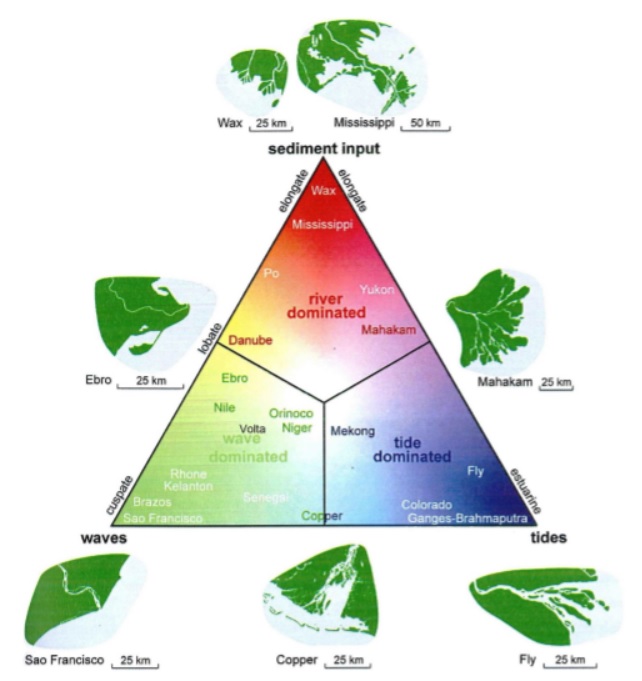
Image 2: Galloway's 1975 delta classification diagram. Acquired from https://pure.tudelft.nl/ws/portalfiles/portal/37464456/Roest_2018_The_coastal_system_of_the_Volta_delta.pdf
From this, it can also be concluded that the Volta delta has to deal with serious coastal erosion. Before the Akosombo dam was built, there was still plenty of sediment that was transported by the river. After construction, this became a lot less because the dam is blocking some of the sediment. As a result, the river can no longer really be seen as a dynamic river delta with lots of sediment.
In addition to the construction of the dam, the wave action of the sea also plays an important role in coastal erosion. This, together with the growing sand ridge, has an impact on the closure of the delta's mouth. The growing sand ridge then has an impact on the biodiversity that lives in the sea.
As the erosion continues, it also has additional consequences for infrastructure and biodiversity, among other things. As a result of the problem, houses have to be demolished, families and communities have to move, some of the infrastructures no longer works and there are problems with agriculture. (Addo, 2015)
Future perspective
In the future, the delta will mainly have to contend with various floods, partly due to erosion and rising sea levels. There are various solutions for this, but not everything will be equally affordable. For example, the idea of protecting the entire coastline is too expensive, but adaptive measures in and around certain regions along the coast are being considered.
Monitoring will also continue to be done with regard to the wave action and various measurements will be made to look at biodiversity.
