Tagus estuary
Deltas
The Tagus is a river that flows through Spain and Portugal. It rises on the slopes of the Muela de San Juan in Spain and flows into the Atlantic Ocean near Lisbon. It is mainly used for agricultural irrigation and generates electricity by means of dams. (Wikipedia, 2021)
Portugal
Before we explain more about the influence of erosion, you might want to get to know Portugal. Portugal is located on the continent of Europe and is part of the Iberian Peninsula.
Portugal is not a large country in itself, but it has a lot to offer. It has a great variety of landscapes and biodiversity. One of the sediments that are strongly present is limestone. This limestone is the result of the accumulation of the remains of organisms that live in the sea.
There is no uniform climate in Portugal and this is due to the fact that the climate responds to vegetation. Portugal, therefore, has three types of climate: the continental climate, the Mediterranean climate, and the Atlantic climate.
Besides the beautiful landscape that is present in Portugal, there are also nice and beautiful cities, such as Porto and Lisbon. Lisbon plays an important role in the economy. In addition, Lisbon is also the city where the Tagus River flows through last. (Smith, 2022)
The graph below shows the average maximum temperature in Portugal in 2017. The data is from Statista and when you scroll over the graph you can see the average temperature for each month.
Impact of erosion
The Tagus estuary ends in the city of Lisbon. As mentioned earlier, limestone is one of the main sediments present in Portugal. However, other sediments are also present. Some examples of sediments that are present in the Tagus estuary are sand and clay. These sediments can be important for agriculture. Agriculture is practiced in the estuary, but rice cultivation is the most prominent. When this cultivation emerges in a Mediterranean climate, irrigation is used. Irrigation also has its drawbacks. Due to the increasing drought, saltwater may dominate the freshwater.
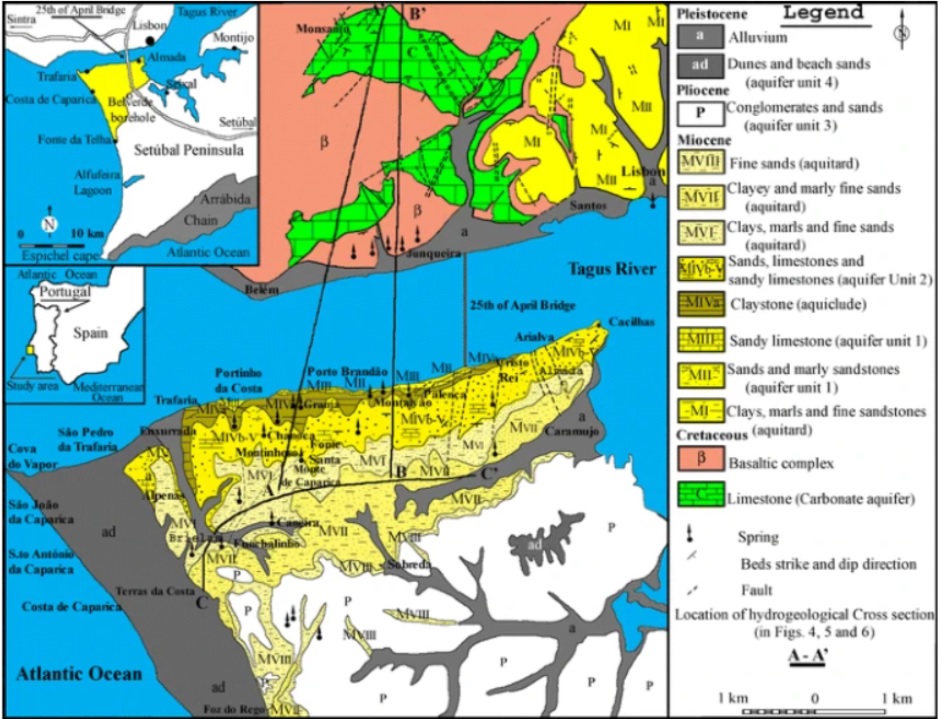
Image 1: Sediments in Portugal. Acquired from https://link-springer-com.aeres.idm.oclc.org/article/10.1007/s10040-009-0450-2

Image 2: Rice cultivation. Acquired from https://unsplash.com/photos/kXoEdaZ3SFw
In addition to the problems of drought and the risk of flooding, there is also the problem of erosion. Erosion is a problem that has been around for several years. In fact, studies carried out in 1998/1999 have shown this to be the case.
Erosion comes in different forms. A study from the 1990s showed that wind erosion is mainly present along with coastal erosion. Wind erosion can carry various small particles and in this way move them to, for example, the interior of Portugal. Coastal erosion is also present due to the waves reaching the coast from the sea. Many estuaries are home to a variety of flora and fauna, such as fish and birds. Mudflats and salt marshes are also present and provide an enhanced effect on biodiversity. The Tagus estuary is therefore a nature reserve where everything comes together and it is still present today.
However, erosion also causes problems. Due to erosion, the marsh areas can disappear and beach erosion causes buildings to have to be demolished, for example, because they are no longer safe at their current location.
